This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful. See our privacy policy.
EA Electronic High Power Density DC Electronic Loads
Conventional and regenerative programmable loads
19 Inch Slide-in Housing
(Series ELR / Regenerative power generation)

Highlights
- Regenerative
- Autoranging
- Color Touchscreen
Technical Specifications
- Power from 80W to 150kW and more
- Voltages 0-10V to 0-2000kV DC
- Current 0-6A to 0-510A (Systems to 3500A)
Features
- Primary clocked, with flexirange or auto-range output
- Externally controlled via analog and digital interfaces
- Permanently integrated interfaces and “plug n play” slot
- State-of-the-art µ-processor control (FPGA)
- Modular highly insulated architecture
- PV (Solar) Array Simulation
- Battery and fuel cell simulation
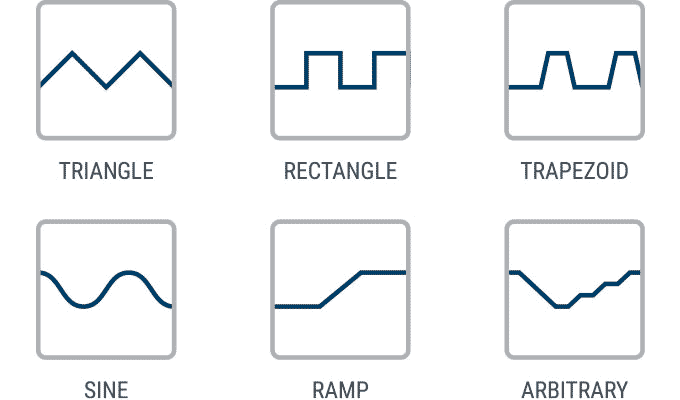
- Function generator sine, rectangle, trapezoid, ramp, arbitrary
- Alarm Management, User Profiles
- For tabletop, 19″ integration and wall mounting
- Analog, Ethernet, USB, CAN, Profibus, GPIB and many more
- Operator Software EA Power Control (Freeware), Multi-Control “App” (license required)
Click below to see our units in 360° view
| Series | Power Connection | Voltage | Current | Power | Datasheet | Get Quote |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EA-ELR 10000 3U | 208-480+10 % 3ph | 80 to 2000V | 0-20A to 0-510A | 5 kW / 10 kW / 15 kW | Get a Quote | |
| EA-ELR 10000 2U | 110-240+10 % 1ph | 0-80V to 0-1500V | 0-6A to +-0-120A | 1500-3000W | Get a Quote | |
| EA-ELR 5000 / ELM 5000 6U | 200-240V~ | 0-80V to 0-200V | 0-12A to 0-25A | 320-3200W | Get a Quote | |
| EA-ELR 10000 4U | 208-480+10 % 3ph | 0-80V to 0-200V | 0-40A to 0-1000A | 30kW | Get a Quote | |
| EA-ELR 9000 HP 3U (EOL) | 380-480V~ | 0-80V to 0-1500V | 0-20A to 0-510A | 5000-15000W | Get a Quote | |
| EA-ELR 9000 3U 208V (EOL) | 220-240V~ 380-415V~ L-N 200-208V~ L-L | 0-80V to 0-1500V | 0-22A to 0-510A | 3100-10500W | Get a Quote |
19 Inch Slide-in Housing
(Series EL / Conventional dissipative)

Highlights
- Autoranging
- Color Touchscreen
- Master-Auxiliary-Bus for Parallel Connection
- Two-quadrant expansion
- 19″ Full slide-in, 2 height units
- Analog und USB Interface
Technical Specifications
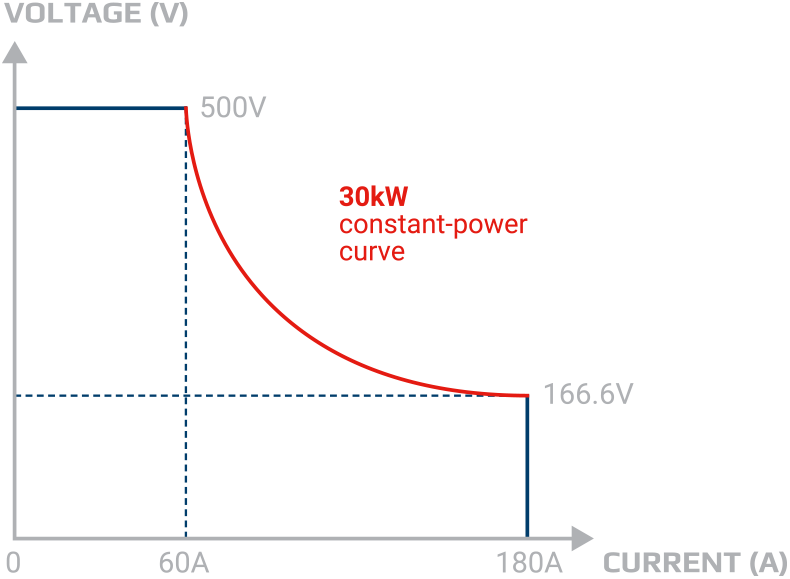
- Power from 300W to 43,2kW (Systems to 227kW and more)
- Voltages 0-80VDC to 0-750VDC
- Current 0-5A to 0-3060A (Systems to 3500A and more)
Features
- Externally controlled via analog and digital interfaces
- Table-top and 19″ rack technology, turnkey system cabinets
- Permanently integrated interfaces and “plug n play” slot for interface retrofitting
- Modular highly insulated architecture, extremely reliable and filtered
- Many interface options: Analog, Ethernet, USB, CAN, Profibus, GPIB and many more
- User software EA Power Control (as freeware and payware)
- Operating modes CV, CC, CP, CR, battery test, MPPT (PV) simulationFor operation on all types of batteries (Pb, NiCa, Li, etc.) as well as photovoltaic (PV) strings, ultracaps, fuel cells, EV motors, alternators and other direct current sources
- Integrated function generator with predefined waveforms such as sine, rectangle, trapezoid, ramp, arbitrary
- Air and water-cooled versions
- Parallel switchable in Master-Auxiliary mode
| Series | Power Connection | Voltage | Current | Power | Design | Datasheet | Get Quote |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EA-EL 9000 B 15U/24U Cabinet | 100-240V~ | 0-80V to 0-750V | 0-3060A | 10800-27000W | Tower | Get a Quote | |
| EA-EL 9000 B 2Q 2U | 100-240V~ | 0-80V to 0-750V | 0-10A to 0-170A | 600-2400W | Tower | Get a Quote | |
| EA-EL 9000 B HP 2U | 100-240V~ | 0-80V to 0-750V | 0-10A to 0-170A | 600-2400W | Tower | Get a Quote | |
| EA-EL 9000 B 3U/6U | 100-240V~ | 0-80V to 0-750V | 0-20A to 0-1020A | 1200-14400W | Tower | Get a Quote |
Space Saving Desktop Style Devices
(Series EL)
| Series | Power Connection | Voltage | Current | Power | Datasheet | Get Quote |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EA-EL 9000 DT | 100-240V~ | 0-80V to 0-750V | 05-A to 0-60A | 400-900W | Get a Quote | |
| EA-EL 3000 B | 100-240V~ | 0-80V to 0-500V | 0-10A to 0-60A | 400W | Get a Quote |
Space-saving Tabletop Devices in Tower Style
(Series EL)
| Series | Power Connection | Voltage | Current | Power | Datasheet | Get Quote |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EA-EL 9000 T | 100-240V~ | 0-80V to 0-500V | 08-A to 0-45A | 400-600W | Get a Quote |
Find the Right Tool

Power Selection Guide
What MUST you consider when choosing a Programmable DC Power Supply? What output is right for your application? How much power you you pay for without over specifying? Download our Guide to help you navigate the many considerations when specing the right DC power supply.
Download Power Guide
FAQs
An electronic load, in the context of electrical engineering, refers to a device designed to simulate the electrical load that a circuit or power source would encounter in a real-world scenario. The load is used for testing and characterizing various electronic components. These components can include power supplies, batteries and voltage regulators.
An electronic load can actively draw current from the device under test (DUT) and provide a controllable load to help operators assess the performance, stability and efficiency of the DUT. An electronic load can help operators evaluate and assess the behavior of electronic and electrical systems that will encounter varying operating conditions.
The electric load of current, otherwise called the electrical current load, refers to the amount of current drawn from a power source by a device or circuit. The electric load of current is typically measured in amperes (A) and represents the flow of electric charge through the load.
The basic electronic load is a simple resistive load, otherwise called a dummy load or fixed load. The basic electronic load consists of resistors that provide a constant resistance value to create a load used to test electronic components and circuits.
A basic electronic load is usually not programmable or adjustable. It serves as a straightforward load for specific resistance testing purposes.
An electronic load bank is a specialized device used to test and validate power sources, such as batteries or generators, to name two. The load bank offers precise and adjustable electrical loads. This allows operators to control the testing of power systems under different conditions. Different industries that benefit from this device include power generation or telecommunications, for example, to help assess equipment performance and capacity.
A DC electronic load is a device designed to simulate and apply controlled electrical loads to direct current (DC) power sources. A DC electronic load enables operators to test and evaluate the performance of DC power supplies, batteries or other DC-powered electronic systems. The device performs this task by drawing specific current levels and enabling precise measurements and assessments.
An example of a DC load is the EA EL Electronic High Power Density DC Electronic Loads from EA Elektro-Automatik, which are designed for “two-quadrant operation,” also called the source-sink principle, which is a combination of a load and a power supply.
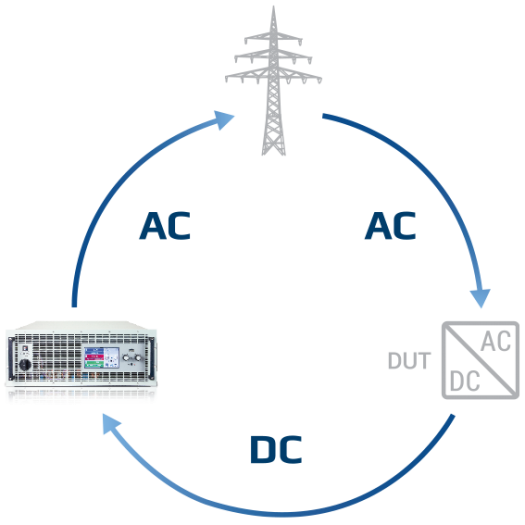
The EA ELR regenerative DC electronic load is a regenerative load that can recover over 96.5% of current back to the local grid, resulting in high energy savings.
In terms of electronic testing and power systems, the DC in DC load stands for direct current. A DC load is a device or component used to apply a controlled electrical load to a DC power source to help operators test and evaluate DC power supplies, batteries or electronic systems.
Several types of DC loads are used in electronic testing and power applications. These include resistive loads with fixed resistance, electronic loads with programmable control, battery simulators for battery behavior, regenerative loads that can absorb and return energy, dynamic loads for simulating real-world applications, and high-power loads designed for testing high-current and high-power electronics. The choice of DC load depends on the testing needs and characteristics of the devices or systems under evaluation.
A programmable DC electronic load is a versatile testing device that applies controlled electrical loads to DC power sources. It allows operators to program the device to simulate various load conditions digitally. It allows operators to adjust current, voltage and other parameters. This makes it a valuable tool to test and characterize power supplies, batteries and electronic components.
To set a DC electronic load, the operator would first input the desired parameters, such as current and voltage limits, using the device controls or a software interface. Once configured, the operator can activate the electronic load to apply the specified load conditions to the DC power source to allow testing and evaluation.
There are different types of DC loads used for testing and evaluation purposes. These include:
- Resistive loads that offer fixed resistance values
- Electronic loads, which are programmable and versatil
- Battery simulators that mimic battery behavior
- Regenerative loads which can absorb and return energy
- Dynamic loads, which can simulate dynamic load profiles, and
- High-power loads that test high-current and high-power electronics
The selection of DC load type will depend on specific testing requirements and the characteristics of the devices or systems that require evaluation.